 On January 22, 2021, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) released a Discussion Paper on “Revised Regulatory Framework for NBFCs- A Scale-Based Approach” on the lines of the announcement made in the Statement on Developmental and Regulatory Policies on December 4, 2020.
On January 22, 2021, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) released a Discussion Paper on “Revised Regulatory Framework for NBFCs- A Scale-Based Approach” on the lines of the announcement made in the Statement on Developmental and Regulatory Policies on December 4, 2020.
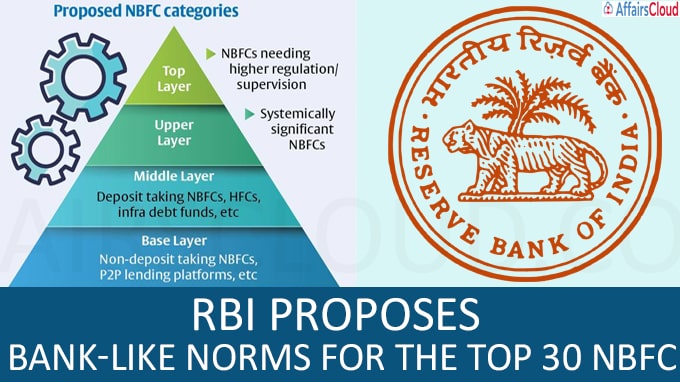
- It envisages a four-layered regulatory and supervisory framework for NBFCs. As per the framework, there will be Bank-like regulations for the top 25 to 30 NBFCs in the country.
- The apex bank has invited comments on the Discussion Paper from NBFCs, market participants and other stakeholders within one month
What is in the new proposed framework?
As per the new framework, the NBFCs will be grouped into four-layers viz. Base Layer (BL), Middle Layer (ML), Upper Layer (UL) and a possible Top Layer (TL).
This grouping is in the form of pyramid which states that there will be least regulatory intervention for NBFCs in BL. As one moves up the pyramid, the regulatory regime will get stricter.
Here is the detail of pyramid:
Base Layer:
This group will consist of NBFCs, currently classified as non-systemically important NBFCs (NBFC-ND/Non-Deposit taking), Peer to Peer lending platforms, Account Aggregators, Non-Operative Financial Holding Company, and NBFCs up to Rs 1,000 crore asset size.
- About 9,209 NBFCs will be in this category.
- The entry point norms will be revised from Rs 2 crore to Rs 20 crore.
- The extant NPA classification norm of 180 days will be harmonized to 90 days.
Middle layer
It will consist of NBFC-ND-SI/Non-Deposit taking-Systemically Important, deposit-taking NBFCs, Housing Finance Companies, Infrastructure Finance Companies, Infrastructure Debt Funds, Standalone Primary Dealers and Core Investment Companies.
- No changes are proposed in capital requirements for NBFC-ML.
- Credit Concentration norms prescribed for NBFC-ML for their lending and investment can be merged into a single exposure limit of 25% for the single borrower and 40% for a group of borrowers.
- These NBFCs should have a Board approved policy on Internal Capital Adequacy Assessment Process (ICAAP). Internal capital can be assessed by factoring credit, market, operational, and all other residual risks.
- An independent Chief Compliance Officer should be appointed, for NBFC’s corporate governance structure.
- As NBFCs have attained a unique business model, therefore their Initial Public Offer (IPO) financing should be put under close scrutiny. In this regard, it is proposed that a limit of Rs 1 crore per individual for any NBFC should be prescribed. The limit for IPO financing in banks is Rs 10 lakh.
Upper Layer
This layer will consist of NBFCs which are identified as systemically significant and can impact financial stability.
- Under this category, the regulatory framework for NBFCs will be bank-like with suitable and appropriate modifications. A total of not more than 25 to 30 NBFCs will occupy this layer.
- A 9% CET (Common Equity Tier) 1 capital will be introduced for NBFC-UL to enhance the quality of regulatory capital.
Top Layer
This top layer of the pyramid will remain empty unless RBI views specific NBFCs catering to this category.
Additional Info:
In 1964, RBI acquired regulatory and supervisory powers over NBFCs with the insertion of Chapter III-B in the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934 (‘RBI Act’).
Recent Related News:
i.RBI will issue guidelines for non-banking financial companies (NBFCs) with regard to distribution of dividend as per a matrix of parameters. Currently there are no guidelines for NBFCs for dividend distribution.
ii.On October 22, 2020, RBI issued the revised regulatory framework for housing finance companies (HFCs) under which the minimum net owned funds (NOF) size for HFCs is fixed at Rs 25 crore.
About Reserve Bank of India (RBI):
Formation– 1 April 1935
Governor– Shaktikanta Das
Headquarters– Mumbai, Maharashtra
Deputy Governors– 4 (Bibhu Prasad Kanungo, Mahesh Kumar Jain, Michael Debabrata Patra, and M Rajeswar Rao)




