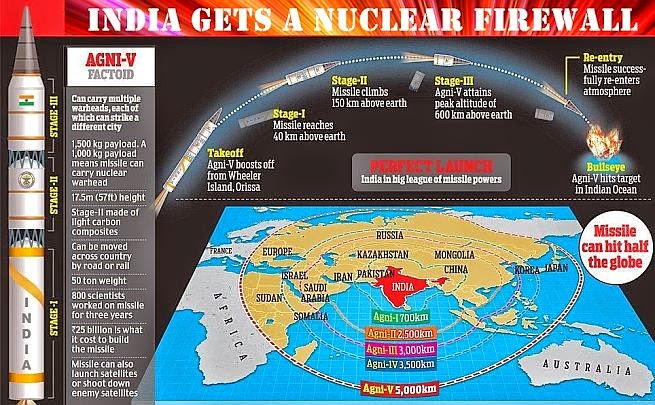
India successfully test-fired its nuclear-capable, Inter-Continental Ballistic Missile (ICBM), the Agni V, on December 26, from Dr Abdul Kalam island, formerly known as Wheeler Island, off the coast of Odisha.
- The three-stage, solid propellant surface-to-surface missile was test-fired from a mobile launcher from launch complex-4 of the Integrated Test Range (ITR) at 11:05 am in Balasore district.
- This was the fourth and final test of the missile. With the success of the final development test, Agni-V is now ready for the induction into the strategic arsenal (collection of weapons) of India.
- The successful induction of Agni V will give India long-range strike capability.
Features of Agni V
The Agni V is India’s indigenously developed intercontinental surface-to-surface nuclear capable ballistic missile with a range of 5,500 to 5,800 km.
- It has been developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation under the Integrated Guided Missile Development Program.
- Agni-V is one of the most advanced missiles which is 17 metres long, 2-metre wide and has launch weight of around 50 tonnes.

- The missile can carry a nuclear warhead of and can carry nuclear warhead of about 1.5 tonnes.
- The missile employs Ring Laser Gyro-based Inertial Navigation System (RINS) and Micro Navigation System (MINS) for navigation, which support the missile to reach the target point within a few metres of accuracy.
- It has the high-speed on board computer and fault tolerant software along with robust and reliable bus to guide the missile flawlessly.
- The Inter-Continental Ballistic Missile (ICBM) Agni-V has the capability to strike targets anywhere in all of Asia and parts of Africa and Europe. Agni-V is capable of striking even the northernmost parts of China
- Once the Agni-V is inducted, India will join the super-exclusive club of countries with ICBMs (missiles with a range of over 5,000-5,500km) alongwith the US, Russia, China, France and the UK.
- It is the fifth variant in the series of medium to long range Agni missiles. Currently, India’s armoury of Agni missile series includes the Agni-1 with 700 km range, Agni-II with 2000 km range, Agni-3 and Agni-4 with with 2,500 km to more than 3,500 range.
- x.The first successful testing of the missile was conducted on 19 April 2012 by DRDO from Wheeler Island off the coast of Orissa, followed by second on September 15, 2013 and third on 31 January 2015.
About DRDO
The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) is an agency of the Republic of India, charged with the military’s research and development, headquartered in New Delhi, India. It is under the administrative control of the Ministry of Defence, Government of India.
- It was formed in 1958 by the merger of the Technical Development Establishment and the Directorate of Technical Development and Production with the Defence Science Organisation.
- Headquarters: New Delhi
- Founded: 1958
- Secretary: Dr.S.Christopher
About Dr. Abdul Kalam Island
Dr. Abdul Kalam Island, formerly known as Wheeler Island, is an island off the coast of Odisha, India, approximately 150 kilometres (93 mi) from the state capital Bhubaneshwar. The Integrated Test Range missile testing facility is located on the island.
- The island was originally named after English commandant Lieutenant Wheeler. On 4 September 2015, the island was renamed to honour the late Indian president, Dr. APJ Abdul Kalam