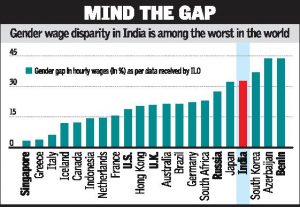
According to the Global Wage Report 2016-17 released by the International Labour Organisation (ILO), India is among one of the World’s worst gender gaps in wages.The report showed that men earned more than women in similar jobs, with the gap exceeding 30 percent. Women are paid 33% less than men in hourly wages in India.
Important points of the report
The report showed that, in India, women represented 63 percent of the lowest paid wage labor while only 15 percent of the highest wage-earners were female.
- Not only were women paid less with wide gender gap at bottom level but there were fewer women in highly paid occupations.
- Among the major economies, Singapore had among the lowest, at 3 per cent while South Korea fared worse than India, with a gap of 37 per cent.
- The report also found that the share of women among wage earners was among the lowest in South Asia. Compared to a global average of 40 per cent, and an Asia-Pacific average of 38 per cent, in South Asia (whose dominant economy is India), only 20 per cent of wage earners were women.

- The report cited a common reason for the wage gap and occupational discrimination to be the choice of education of women. For instance nursing or any other care work is generally seen as profession represented by women. Due to the higher representation of women in such sectors, their work is undervalued resulting in a gender pay gap.
- Based on the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) studies, the report found that strong labour market institutions and policies such as collective bargaining and minimum wages lowered the pay gap.
- The gender pay gap was found to be smallest (8 per cent) in the group of countries where the collective bargaining rate is at least 80 per cent, and widest in countries with weak collective bargaining and no or very low minimum wages.
- In India, in the area of high income inequality, the top one percent earned 33 times what the bottom 10 per cent did. The top 10 per cent also earned 43 per cent of all wages.
- However, the report also highlighted a positive aspect that average wages grew by 60% in India since 2006 and wage inequality decreased. The average wage more than doubled in China in last decade.
About ILO Global Wage 2016 Report
ILO Global Wage Report contributes to the United Nations 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development by making comparative data and information on recent wage trends available  to governments, social partners, academics and the general public.
to governments, social partners, academics and the general public.
- These trends show that global real wage growth dropped sharply during the post-2008 economic crisis, recovered in 2010, but has since decelerated.
- More specifically, the report analyses the extent to which overall wage inequality is the result of wage inequality between enterprises and wage inequality within enterprises.
About ILO
The International Labour Organization (ILO) is a United Nations agency dealing with labour issues, particularly international labour standards, social protection, and work opportunities for all.
- The ILO has 187 member states: 186 of the 193 UN member states plus the Cook Islands are members of the ILO.
- The ILO registers complaints against entities that are violating international rules; however, it does not impose sanctions on governments.
- In 1969, the organization received the Nobel Peace Prize for improving peace among classes, pursuing decent work and justice for workers, and providing technical assistance to other developing nations.
Keys :
- Formation: 1919
- Headquarters: Geneva, Switzerland
- Head: Guy Ryder