Hello Aspirants,
Welcome to Banking Awareness Quiz in AffairsCloud.com. Here we are creating quiz covering important questions which are common for all the bank exams and other competitive exams.
- What is the full form of FCCB?
A. Foreign Currency convertible Bond
B. Foreign Currency credit Bond
C. Financial Consortium and Credit Bureau
D. Future Credit and Currency Bureau
E. None of the AboveA. Foreign Currency convertible Bond
Explanation:
Foreign currency convertible bonds (FCCBs) are a special category of bonds. FCCBs are issued in currencies different from the issuing company’s domestic currency. A convertible bond is a mix between a debt and equity instrument. - What is the ceiling on amount of Insured deposits kept by one person in different branches of a bank?
A. Rs.25000
B. Rs.50000
C. Rs.75000
D. Rs.1,00,000
E. Rs.2,00,000D. Rs.1,00,000
Explanation:
The deposits kept in different branches of a bank are aggregated for the purpose of insurance cover and a maximum amount upto Rupees one lakh is paid. - Which of the following institutions is responsible for the supervision of RRBs?
A. RBI
B. SEBI
C. NABARD
D. GOI
E. Both (A) and (C)E. Both (A) and (C)
Explanation:
NABARD has been sharing with the Reserve Bank of India certain supervisory functions in respect of cooperative banks and Regional Rural Banks (RRBs). - By which rate is the domestic current rate of currency converted into foreign currency?
A. Bank Rate
B. CRR
C. Stock Exchange Rate
D. Repo Rate
E. Exchange RateE. Exchange Rate
Explanation:
An exchange rate aka a (foreign-exchange rate, forex rate, FX rate or Agio) between two currencies is the rate at which one currency will be exchanged for another. It is also regarded as the value of one country’s currency in terms of another currency. - Which of the following works is/are done by Credit Information Companies?
A. Collecting records of an individual’s payments pertaining to loans
B. Maintaining records of an individual’s payments pertaining to credit cards
C. Creating Credit Information Reports
D. All of the Above
E. None of the AboveD. All of the Above
Explanation:
Credit Information Companies collects and maintains records of an individual‘s payments pertaining to loans and credit cards. These records are submitted to Credit Information Companies by banks and other lenders, on a monthly basis. This information is then used to create Credit Information Reports (CIR) and credit scores which are provided to lenders in order to help evaluate and approve loan applications. - Which of the following was the first credit rating agency of India?
A. CIBIL
B. Equifax
C. CRISIL
D. ICRA
E. ExperianA. CIBIL
Explanation:
Credit Information Bureau (India) Ltd; CIBIL is India’s first Credit Information Company, also commonly referred as a Credit Bureau. We collect and maintain records of individuals’ and non-individuals’ (commercial entities) payments pertaining to loans and credit cards. These records are submitted to us by banks and other lenders on a monthly basis; using this information a Credit Information Report (CIR) and Credit Score is developed, enabling lenders to evaluate and approve loan applications. A Credit Bureau is licensed by the RBI and governed by the Credit Information Companies (Regulation) Act of 2005. - The largest shareholder of a nationalized bank is_______
A. RBI
B. Government of India
C. NABARD
D. All of the Above
E. None of the AboveB. Government of India
Explanation:
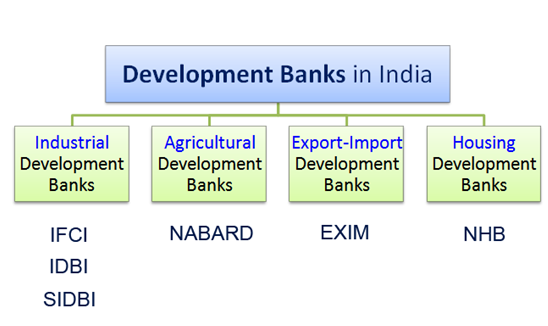
Public Sector Banks (PSBs) are banks where a majority stake (i.e. more than 50%) is held by a government.The shares of these banks are listed on stock exchanges. There are a total of 27 PSBs in India [21 Nationalized banks + 6 State bank group (SBI + 5 associates)]In 2011 IDBI bank and in 2014 Bharatiya Mahila Bank were nationalized with a minimum capital of Rs 500 crore. - Which of the following comes under the category of Development Banks?
A. Industrial Development Banks
B. Agricultural Development Banks
C. Housing Development Banks
D. Export-Import Development Banks
E. All of the AboveE. All of the Above
Explanation:

- With which article of the Indian Constitution is Money Bill related?
A. Article 110
B. Article 109
C. Article 108
D. Article 107
E. None of the AboveA. Article 110
Explanation:
Under Article 110(1) of the Constitution, a Bill is deemed to be a Money Bill if it contains only provisions dealing with all or any of the following matters:
(a) the imposition, abolition, remission, alteration or regulation of any tax;
(b) regulation of borrowing by the government;
(c) custody of the Consolidated Fund or Contingency Fund of India, and payments into or withdrawals from these Funds;
(d) appropriation of moneys out of the Consolidated Fund of India;
(e) declaring of any expenditure to be expenditure charged on the Consolidated Fund of India or the increasing of the amount of any such expenditure;
(f) receipt of money on account of the Consolidated Fund of India or the public account of India or the custody or issue of such money or the audit of the accounts of the Union or of a State; or
(g) any matter incidental to any of the matters specified in sub-clauses (a) to (f). - CGTMSE stands for _______
A. Central Government Fund Trust for Medium and Small Enterprises
B. Central Government Fund Transfer fund for Medium and Small Enterprises
C. Central Government Fund for Medium Size Enterprises
D. Credit Guarantee Fund Trust for Micro and Small Enterprises
E. None of the AboveD. Credit Guarantee Fund Trust for Micro and Small Enterprises
Explanation:
Government of India and SIDBI set up the Credit Guarantee Fund Trust for Micro and Small Enterprises (CGTMSE).
The main objective is that the lender should give importance to project viability and secure the credit facility purely on the primary security of the assets financed. The other objective is that the lender availing guarantee facility should endeavor to give composite credit to the borrowers so that the borrowers obtain both term loan and working capital facilities from a single agency.
AffairsCloud Recommends Oliveboard Mock Test
AffairsCloud Ebook - Support Us to Grow
Govt Jobs by Category
Bank Jobs Notification