On December 20, 2019, India’s central bank, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has decided to conduct simultaneous sale and purchase of government bonds under the Open Market Operations (OMO) mechanism, a concept similar to “Operation Twist” that was last adopted by the US (United States) Federal Reserve in 2013.
So, the RBI will buy bonds worth Rs 10,000 crore of 6.45% maturing in the year 2029 and issuing bonds worth Rs 10,000 crore maturing in the year 2020.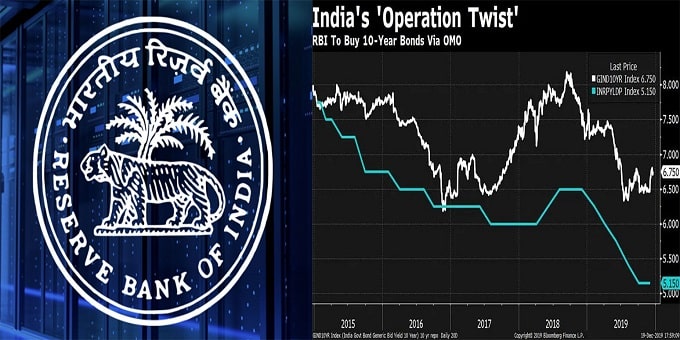 Key Points:
Key Points:
i.This decision will reduce interest rates on long-term bonds & improve the liquidity position in the market. Currently, the difference between the repo rate and the interest rate payable on long-term bonds is around 1.50 % (or 150 bps -basis points).
ii.By lowering the interest rates payable on long-term government bonds, central banks pave the way for lowering long-term interest rates because interest rates for long-term debt are also based on the interest rates payable on government securities.
iii.If RBI continues such an operation twist even further, it will help in reducing the rates of fixed long term loans that will open the way for the industry to get loans at rates lower than the current rate, which will make it easier for them to expand their business.
iv.Background: The benchmark 10-year yield had increased as much as 37 bp to 6.84% from its level. It is currently still up 28 bps.
Operation Twist:
It is the name given to a monetary policy tool that the Jerome Powell-led US Federal Reserve had started to influence the rate of interest in the world’s largest economy. The process involves buying & selling of both short- and long-term government bonds .The method was later adopted by several other central banks.
About OMO:
It is the sale and purchase of government securities and treasury bills by RBI to regulate the money supply in the economy. When the RBI wants to increase the money supply in the economy, it purchases the government securities (G-Secs) from the market and it sells them to suck out liquidity from the system.
About RBI:
Headquarters– Mumbai, Maharashtra
Formation– 1 April 1935
Governor– Shaktikanta Das
Deputy Governors– 4 (BP Kanungo, N S Vishwanathan, Mahesh Kumar Jain, 1 is yet to be appointed)




