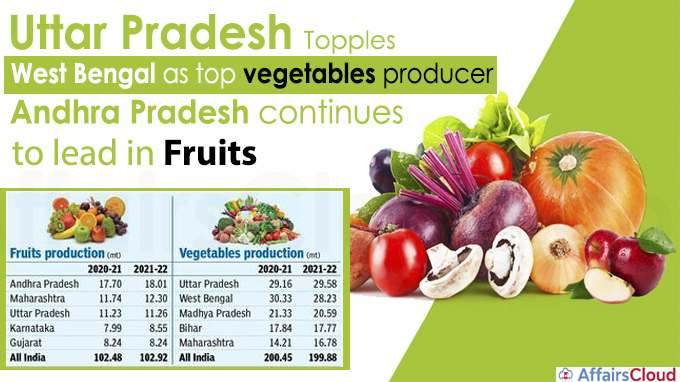
Uttar Pradesh (UP) has become the top producer of vegetables, getting back its first position by demoting West Bengal to the second position, with a difference of a million tonnes in production in 2021–22 Crop Year (CY) (July–June), after two years since 2020. On the other hand, Andhra Pradesh remains the top fruit producer.
- India’s horticulture output is likely to drop marginally by 0.4% to 333.25mt in 2021–22 from the previous year (2020–21) as production of vegetables, spices, and plantation crops is set to decline.
- Among the key essential items, while potato and tomato production are expected to decline, onion production is expected to increase.
Vegetable Production:
i.Vegetable production in Uttar Pradesh is estimated to be 29.58 million tonnes (mt) in the 2021–22 crop year (July–June), down from 29.16 mt in 2020–21, while West Bengal output is expected to dip to 28.23 mt in 2021-22 from 30.33 mt in 2020-21.
ii.Other top producers of vegetables as per the data in the current year 2021-22 include Madhya Pradesh at 20.59 mt, Bihar at 17.77 mt and Maharashtra at 16.78 mt.
Top 3 States/UT in Vegetable Production for the FY2021-22:
| Rank | State | Production in MT |
| 1 | Uttar Pradesh(UP) | 29.58 |
| 2 | West Bengal(WB) | 28.23 |
| 3 | Madhya Pradesh | 20.59 |
Fruit Production:
i.In 2021–22, Andhra Pradesh is expected to produce 18.01 million tonnes of fruit, up from 17.7 million tonnes in 2020–21.
ii.Maharashtra is anticipated to produce 12.3 million tonnes of fruit, up from 11.74 million tonnes in 2020–21.
iii. Other top producers of fruits are Uttar Pradesh at 11.26 mt, Karnataka at 8.55 mt, and Gujarat at 8.24 mt. Incidentally, Gujarat’s production has remained unchanged from 2020-2021.
Top 3 States/UT in Fruit Production for the FY2021-22:
| Rank | State | Production in MT |
| 1 | Andhra Pradesh (AP) | 18.01 |
| 2 | Maharashtra | 12.30 |
| 3 | Uttar Pradesh (UP) | 11.26 |
iv.The Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) has taken several initiatives to encourage apple production in warmer regions. For this reason, the Central Institute of Temperate Horticulture (CITH) in Srinagar (Jammu & Kashmir) has found low-chill apple types such as Anna, Dorsett Golden, Mayan, and Michael and has started reproducing them.
Measures by The Government of India (GoI) To Leverage the Horticulture Production:
Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH) scheme:
i.It is a centrally sponsored scheme (CSS) implemented by the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare (MoA&FW) from 2014-15.
ii.It is launched with an objective to have holistic growth of the horticulture sector covering fruits, vegetables, root and tuber crops, mushroom, spices, flowers, aromatic plants, coconut, cashew and cocoa.
iii. MIDH has the following sub-schemes as its component:
- National Horticulture Mission (NHM)
- Horticulture Mission for North East & Himalayan States (HMNEH)
- National Horticulture Board (NHB)
- Coconut Development Board (CDB)
- Central Institute for Horticulture (CIH), Nagaland.
iv.Production of fruits and vegetables are supported under the Area Expansion component of the MIDH scheme, which is implemented through State Horticulture Missions (SHMs).
NOTE: Horticulture: – It is a science, as well as, an art of production, utilization and improvement of horticultural crops, such as fruits and vegetables, spices and condiments, ornamental, plantation, medicinal and aromatic plants.




