A mutual fund is a professionally managed investment fund that pools money from many investors to purchase securities. They are professionally managed in a way that when people invest in the mutual funds, they get the services of a team of professionals.
- By investing in mutual fund, one can gain the services of professional fund managers, who would otherwise be costly for an individual investor.
- Professional fund managers can assess the risk profile of the investments.
- Without investing a large amount of money, one can enjoy the services.
- Since many investors are investing small amounts in a single mutual fund, risk (if any) gets divided among all of them, so mutual funds are better options for investments.
- Investments in a stock market go up or down with the change in prices of the stocks, so the biggest risk in investing in Mutual Funds is the market risk because of the economic alterations.
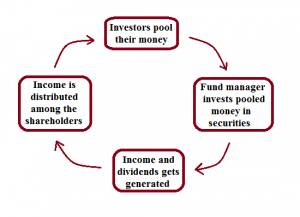
An investment in mutual fund follows the following cycle:

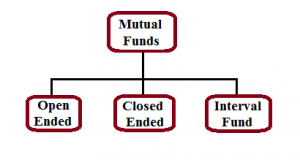
Open Ended:
Under this scheme, the investors are free to buy or sell units at any point in time. This means that they do not have a maturity date. So your money is available to you any time you want.
As new investors can purchase fresh units any day, the unit capital is case of an open-ended funds can fluctuate on daily basis.
Closed Ended:
Under this scheme, there is a stipulated maturity period. The investors can invest only during the launch period known as the NFO (New Fund Offer) period. Unlike open-ended funds, unit capital in case of closed-ended funds does not fluctuate on daily basis.
Interval Fund:
This is a scheme which operates as a combination of open and closed ended schemes. It allows investors to trade units at pre-defined intervals.
Various types of equity and debt mutual funds available in India:
1. Equity or growth schemes
They are most popular MF(Mutual Fund) schemes. They allow investors to participate in stock markets. The scheme has high investment risks, but at the same time also have a high return potential in the long run. They are more suitable for long term investments. Normally an equity fund or diversified equity fund as it is commonly called invests over a range of sectors to distribute the risk.
Equity funds can be further divided into three categories. They are
- Sector-specific funds: These are mutual funds that invest in a specific sector like infrastructure, banking, mining, etc. or specific segments like mid-cap, small-cap or large-cap segments. They are suitable for investors having a high risk appetite and have the potential to give high returns.
- Index funds: Index funds are ideal for investors who want to invest in equity mutual funds but at the same time don’t want to depend on the fund manager. An index mutual fund follows the same strategy as the index it is based on.
- Tax saving funds: These funds offer tax benefits to investors. They invest in equities and are also called Equity Linked Saving Schemes (ELSS). These types of schemes have a 3 year lock-in period. The investments in the scheme are eligible for tax deduction u/s 80C of the Income-Tax Act, 1961.
2. schemes Money market funds or liquid funds:
These funds invest in short-term debt instruments, looking to give a reasonable return to investors over a short period of time. These funds are suitable for investors with a low risk appetite who are looking at parking their surplus funds over a short-term. These are an alternative to putting money in a savings bank account.
3. schemes Fixed income or debt mutual funds:
These funds invest a majority of the money in debt – fixed income i.e. fixed coupon bearing instruments like government securities, bonds, debentures, etc. They have a low-risk-low-return outlook and are ideal for investors with a low risk appetite looking at generating a steady income. However, they are subject to credit risk.
4. schemes Balanced funds:
As the name suggests, these are mutual fund schemes that divide their investments between equity and debt. The allocation may keep changing based on market risks. They are more suitable for investors who are looking at a combination of moderate returns with comparatively low risk.
5. schemes Hybrid/ Monthly Income Plans (MIP):
These funds are similar to balanced funds but the proportion of equity assets is lesser compared to balanced funds. Hence, they are also called marginal equity funds. They are especially suitable for investors who are retired and want a regular income with comparatively low risk.
6. schemes Gilt funds:
These funds invest only in government securities. They are preferred by investors who are risk averse and want no credit risk associated with their investment. However, they are subject to high interest rate risk.


