 On March 23, 2021, the Reserve Bank of India(RBI) issued RBI (Amalgamation of Urban Cooperative Banks) Directions, 2020, guidelines for merger/amalgamation to all Primary/Urban Co-operative Banks(UCBs) to place them in the public domain.
On March 23, 2021, the Reserve Bank of India(RBI) issued RBI (Amalgamation of Urban Cooperative Banks) Directions, 2020, guidelines for merger/amalgamation to all Primary/Urban Co-operative Banks(UCBs) to place them in the public domain.
Objective: To provide an avenue for the non-disruptive weak UCB sector by consolidating them with the strong one in that sector.
Three circumstances under the Directions:
As per the ‘Amalgamation of Urban Cooperative Banks, Directions, 2020’, the proposals for merger and amalgamation among UCBs will be considered under three circumstances
1.when the net worth of the amalgamated bank is positive, and the amalgamating bank assures to protect the entire deposits of all depositors of the amalgamated bank.
2.when the net worth of an amalgamated bank is negative and the amalgamating bank on its own assures to protect deposits of the depositors of the amalgamated bank.
3.when the net worth of the amalgamated bank is negative, and the amalgamating bank assures to protect the deposits of all depositors of the amalgamated bank, with the financial support from the State government, extended upfront as part of the process of merger.
Who will Approve the Amalgamation?
- RBI has the discretionary powers to approve the voluntary amalgamation of UCBs under the provisions of Section 44A read with Section 56 of the Banking Regulation Act, 1949 which is amended by, Banking Regulation (Amendment) Act 2020.
- The amalgamation shall be approved by a two-thirds majority of the total number of board members of both amalgamating and amalgamated UCBs, and not just of those present and voting.
Who can merge?
- A cooperative bank can merge only with another cooperative bank situated in the same state or with a cooperative bank registered under the Multi-State Cooperative Societies Act.
Key point:
- In April 2015 RBI has placed 52 UCBs under All Inclusive Directions(AID)for 5 years (from April 1, 2015, till December 11, 2020)
- The amalgamating bank will be permitted to retain the facilities such as Authorized Dealer(AD) category I license issued under FEMA
- Higher level of Capital to Risk Weighted Assets Ratio (CRAR) at 12 % is required on an on-going basis, provided the amalgamating bank maintains the RBI’s benchmark CRAR of 9%.
- According to the RBI’s latest ‘Report on Trend and Progress of Banking in India’, As of March-end 2020, there were 1,539 UCBs in India.
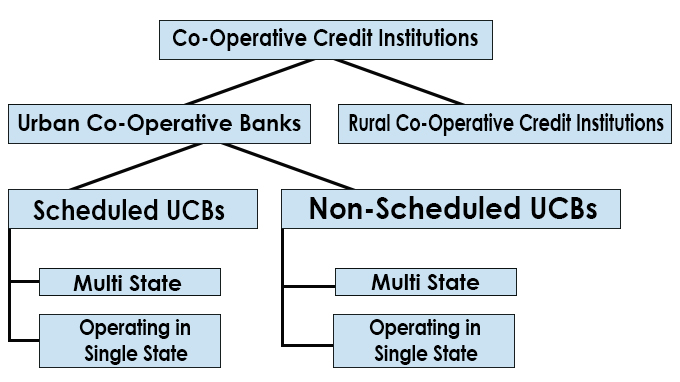
Structure of Co-operative Banks in India:
 Recent Related News:
Recent Related News:
On February 18, 2021, The Reserve Bank of India(RBI) on considering the present liquidity position of Deccan Urban Co-operative Bank Ltd., has imposed a withdrawal cap of Rs 1,000 on the customers of the bank. But, customers are allowed to set off loans against deposits subject to conditions. This is for the period of 6 months from the close of business on February 19, 2021.
About Co-operative Banks:
Co-operative banks in India are registered under the States Cooperative Societies Act and they are regulated by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and governed by
- Banking Regulations Act 1949 and,
- Banking Laws (Co-operative Societies) Act, 1955.




