As per the latest health survey by the government, India’s health index has shown a notable improvement over the last decade including an improvement in sex ratio at birth and a decline in infant mortality rate.
- The latest National Family Health Survey-4 (NFHS-4) conducted for year 2015-16 was unveiled by Health Ministry in New Delhi.
- The report is based on the information collected from 6 lakh households, 7 lakh women and 1.3 lakh men and for the first time provides district level estimates.
- The results show that if proper investment are made and good programmes are designed in health sector, then required result will also be seen.
Key Features of National Family Health Survey-4 (NFHS-4)
1.Infant Mortality Rate
Infant mortality rate (IMR) is the number of deaths of children with age less than one year per 1000 live births.
- As per the survey report, the Infant Mortality Rate (IMR) saw a decline from 57 to 41 per 1,000 live births between NFHS-3 (2005-06) and NFHS-4
- The IMR declined substantially in almost all the states during the last decade but dropped by more than 20 percentage points in Tripura, West Bengal, Jharkhand, Arunachal Pradesh, Rajasthan and Odisha.
- Besides, when compared to NFHS-1, the IMR substantially declined from 79 per 1,000 live births in NFHS-1 (1992-93) to 41 per 1,000 live births in NFHS-4.
2.Sex Ratio at Birth
As per the survey, the sex ratio at birth (number of females per 1,000 males) improved 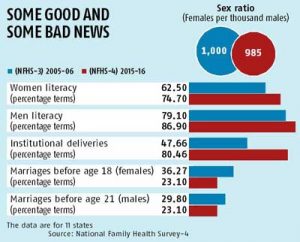 from 914 to 919 at the national level over the last decade with the highest in Kerala (1,047), followed by Meghalaya (1,009) and Chhattisgarh (977).
from 914 to 919 at the national level over the last decade with the highest in Kerala (1,047), followed by Meghalaya (1,009) and Chhattisgarh (977).
- Haryana also witnessed a significant increase from 762 to 836.
3.Institutional Births
The institutional births increased by 40 percent from 38.7 percent in NFHS-3 to 78.9 percent in NFHS-4.
- The survey also noted that there was an increase of 34.1 percent institutional births in public facility. The Empowered Action Group (EAG) in Assam also experienced more than a 40 percent increase.
- The proportion of women who received at least 4 antenatal care visits for their last birth increased by 14 percent points from 37 percent to 51.2 percent over the decade (2005-15), while there has been a substantial increase of 20 or more percentage points in seven states.
4.Total Fertility Rate
The Total Fertility Rate (TFR) declined to 2.2 children per woman from 2.7 in NFHS-3. This rate shows that the country is moving closer to target level of 2.1.
- The survey found that there was considerable decline in the TFR in each of the 30 states in India.
- The maximum decline was observed in Uttar Pradesh (1.1 child) followed by Nagaland (1.0 child), Arunachal Pradesh and Sikkim (0.9 child each). Bihar, however, failed to register substantial decline.
5.Immunization
The report stated that the Children within the age of 12-23 months have been fully immunized (BCG, measles and 3 doses each of polio).
- The DPT (diphtheria, pertussis (whooping cough), and tetanus) immunization saw an increase of 18 percentage points from 44 percent in NFHS-3 to 62 percent in NFHS-4,
- The survey found that the full immunization coverage increased in Punjab, Bihar and Meghalaya by 29 percentage point each, while in Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, Jharkhand and Chhattisgarh it increased by 28 percentage points each.
About National Family Health Survey
The National Family Health Survey (NFHS) is a large-scale, multi-round survey conducted using selective sample of households throughout India.
- The NFHS is a collaborative project of the International Institute for Population Sciences (IIPS),Mumbai, India; ORC Macro, USA and the East-West Center, USA.
- NFHS is funded by the United States Agency for International Development (USAID) with supplementary support from United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF).
- The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MOHFW), Government of India, designated
- The First National Family Health Survey (NFHS-1) was conducted in 1992-93, NFHS-2 in 1998-99 and NFHS-3 in 2005-2006





