Revolt of 1857 has a significant importance in Indian History. This revolt is called as “first war of Independence” by some historians. This revolt was not because of immediate reactions by Indians, but due to oppression carried out by Britishers for more than a century.

Following is the time line of historical events which led a way toward India’s first war of independence:
Event 1(1773): First Governor General
 Lord Warren Hastings became the first Governor General of Bengal. Hewas called as first Governor General of India (don’t confuse it with Governor General of India because Governor General of India was firstly declared in 1833.Till 1833 governor general of Bengal was considered as head of India).
Lord Warren Hastings became the first Governor General of Bengal. Hewas called as first Governor General of India (don’t confuse it with Governor General of India because Governor General of India was firstly declared in 1833.Till 1833 governor general of Bengal was considered as head of India).
Event 2(1793):Permanent Settlement
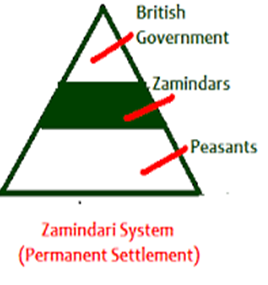
Permanent settlement was introduced into some parts of India,which was also known as “Zamindari System”.Lord Cornwallis was the Governor General at that time.This system was very suppressing and forced farmers to pay taxes even in the dry season.
Under this system, The Zamindars were made hereditary owners of the land under their possession. They and their successors exercised total control over lands. The company’s share in the revenue was fixed permanently with the Zamindars.
Event 3(1799): Subsidiary Alliance System
 Subsidiary Alliance system was passed by Lord Wellesley,under which Indian princely states had to come directly under the British Empire.Their army supposed to be trained by Britishers; no relation with European countries and finance department of princely state should be held by a British only.This system produced discomfort among Indian princes. Nizamalikhan, Nawab of Hyderabad was the first to sign.
Subsidiary Alliance system was passed by Lord Wellesley,under which Indian princely states had to come directly under the British Empire.Their army supposed to be trained by Britishers; no relation with European countries and finance department of princely state should be held by a British only.This system produced discomfort among Indian princes. Nizamalikhan, Nawab of Hyderabad was the first to sign.
Event 4(1829): Ban On Sati

Ban on sati was accepted by the Britishers after the effort of Raja Ram Mohan Roy. Lord William Bentinck was the governor general at this time. Lord William Bentinck was the first governor general of India. Sati was an archaic Indian funeral custom where a widow immolated herself on her husband’s pyre, or committed suicide in another fashion shortly after her husband’s death.
Event 5(1835): Education policy of Britishers

Lord Macaulay introduced new English education system through English education act, 1835. The main aim of this policy was to replace old and ancient education system which strengthens Indian culture with new English system which made British culture supreme.
Event 6 (1848): Doctrine of lapse
 Doctrine of lapse introduced by Lord Dalhousie, under which princely states without a heir had to merge their empires with British Empire. Satara was the first state to merge with Britishers under doctrine of lapse.
Doctrine of lapse introduced by Lord Dalhousie, under which princely states without a heir had to merge their empires with British Empire. Satara was the first state to merge with Britishers under doctrine of lapse.
Event 7(1856): Widow Remarriage Act and Religious Diability Act
Widow Remarriage act was passed by Lord Dalhousie with the efforts of Iswar Chandra vidyasagar in 1856.
Lord Dalhousie was replaced by Lord Canning .He passed theReligious Disability Act, 1856, under which if anyone converts his/her religion, their parents cannot disown him/her from their property. This was simply to promote christianity.
Final Event
There was a news in military that the newly introduced Enfieldrifles ‘cartilage seal was made of cow’s or pig’s flesh, there were also news regarding mixing of animal bones into flour.19th infantry from Bengal started this revolt. This was immediately followed by revolt of 34thinfantry,Mangalpandey was from this battalion. The revolt began, and Bahadur shah Zafar,last king of mughal empire was declared as the leader. But this revolt came to an end after one year. It is also referred as “India’s first war of Independence”( Ref: V.D Savarkar book).
So we can conclude that 1857 revolt was not due to enfield rifles issue but because of culmination of various factors which were seen by Indians as an intrusion in their culture, political space, economical activities, religion and personal life.
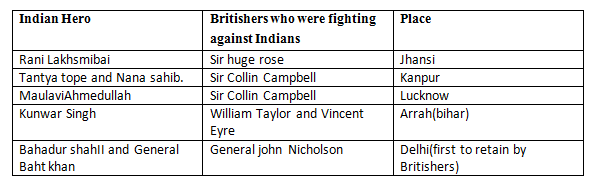
Heroes of 1857 revolt: