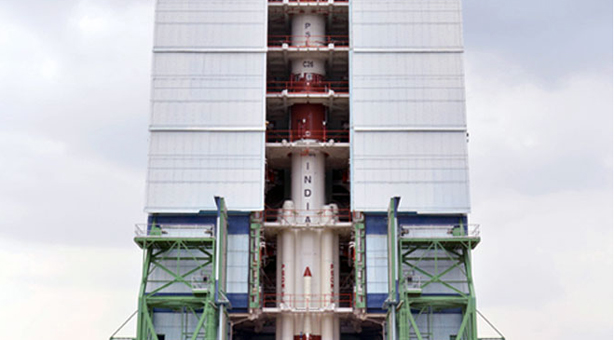
ISRO successfully launched IRNSS-1C, the third satellite of the seven satellite series of the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System. India moved nearer to a selected group of space-faring nations having such a system.
The Satellite was carried by Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) – C26, which is lifted off from the first launch pad of Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota. IRNSS-1C is the first geostationary satellite in the IRNSS system.
Payloads:
The satellite has two kinds of payloads – navigation and ranging.
- The navigation payload would transmit navigation service signals to the users.
- The ranging payload consists of C-band transponder which facilitates accurate determination of he range of the satellite.
The IRNSS 1C will be utilized for two services- Standard Positioning Service (SPS) extended to all users and Restricted Service (RS) which will be encrypted.
The fourth navigational satellite of the IRNSS segment will be launched in December, and the project will be fully operational next year.
For the first time that India has conducted four orbital launches in one calendar year.
- GSAT-14 by a GSLV in January
- IRNSS-1B by a PSLV in April
- SPOT-7 by a PSLV in June
- IRNSS-1C by a PSLV in April
A fifth launch is tentatively scheduled for December, with another PSLV deploying the fourth IRNSS satellite, IRNSS-1D.
The Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle,usually known by its abbreviation PSLV is the first operational launch vehicle of ISRO. PSLV is capable of launching 1600 kg satellites in 620 km sun-synchronous polar orbit and 1050 kg satellite in geo-synchronous transfer orbit. The reliability rate of PSLV has been superb. There had been 27 continuously successful flights of PSLV, till October 2014 .
PSLV has rightfully earned the status of workhorse launch vehicle of ISRO. PSLV has repeatedly proved its reliability and versatility by launching 71 satellites / spacecrafts ( 31 Indian and 40 Foreign Satellites) into a variety of orbits so far.
Source ISRO