- Robert Hook was the first to coin the term ‘Cell’
- Cell is defined as structural and functional unit of the body
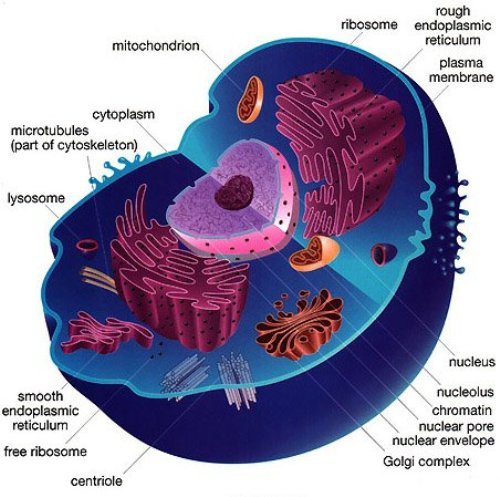
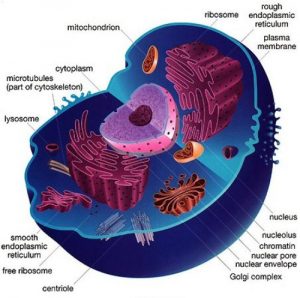 PROTOPLASM
PROTOPLASM
- It is the living substance of the cell. It is a viscous, colourless fluid and is the seat for all physiological functions.
ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM
- The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of membranes found throughout the cell and connected to the nucleus. The membranes are slightly different from cell to cell and a cell’s function determines the size and structure of the ER
RIBOSOMES
- They are the smallest organelles of the cell
- Ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis in the cell
GLOGI COMPLEX (DICTYOSOMES)
- The main function of Golgi complex is cell secretion e. it packs and transports certain materials like proteins and polysaccharides out of the cells.
- It is involved in the formation of primary lysosmes
MITOCHONDRIA
- Mitochondrion are called ‘power house of the cell’.
PLASTIDS
The plastids are of three types :-
- Leucoplast
- Chromoplast
- Chloroplast
- Leucoplasts are colourless plastids, found in the underground parts of plants which are not exposed of light.
- Chromoplasts are orange, yellow or red coloured plastids found in petals, fruits and roots in certain higher plants. The red colour of ripe tomatoes is the result of Chromoplasts which contain the red pigment lycopene
- Chloroplasts are the most important and most common plastids found in all the photosynthesising cells except prokaryotes. Blue-green algae however, lacks chloroplasts
LYSOSOMES : are also called suicidal bags as when these are injured by a toxic substance, the enzymes thus released can digest the whole cell.
AffairsCloud Recommends Oliveboard Mock Test
AffairsCloud Ebook - Support Us to Grow
Govt Jobs by Category
Bank Jobs Notification