 According to the World Economic Forum(WEF)’s Global Gender Gap Report 2024, India closed 64.1% of its gender gap in 2024 with a population of over 1.4 billion and secured the 129th rank among 146 countries in the Global Gender Gap Index 2024.
According to the World Economic Forum(WEF)’s Global Gender Gap Report 2024, India closed 64.1% of its gender gap in 2024 with a population of over 1.4 billion and secured the 129th rank among 146 countries in the Global Gender Gap Index 2024.
- Iceland has topped the 2024 Index followed by Finland and Norway in 2nd and 3rd positions respectively.
Note: The 2024 Index, the 18th edition of the Global Gender Gap Index, benchmarks gender parity across 146 economies, providing a basis for the analysis of gender parity developments across two-thirds of the world’s economies.
- For the first time Sudan and Uzbekistan are included in the index.
Top 5 on Global Gender Gap Index 2024:
| Rank | Country | Score 0-1 |
|---|---|---|
| 129 | India | 0.641 |
| 1 | Iceland | 0.935 |
| 2 | Finland | 0.875 |
| 3 | Norway | 0.875 |
| 4 | New Zealand | 0.835 |
| 5 | Sweden | 0.816 |
Key Points:
i.India has dropped by 2 ranks lower than the 2023 index with a marginally lower score (0.17 % points). this is primarily due to a slight decline in ‘Educational Attainment’ and ‘Political Empowerment,’ parameters, while ‘Economic Participation’ and ‘Opportunity’ scores slightly improved.
ii.According to the report, the world has closed 68.5 per cent of the gender gap, but looking at the current scenario, it will take another 134 years – equivalent to five generations to achieve full gender parity. Subindex Analysis for India
Subindex Analysis for India
i. India’s scored 4% in ‘Educational Attainment’, lower compared to a score of 100% in 2023.
- The shares of women are high in primary, secondary and tertiary education enrolments and gradually increasing.
- India is ranked No.1 on gender parity in terms of enrolment in secondary education, it is ranked 105th in tertiary enrolment, 124th on literacy rate and 89th in primary education enrolment.
ii.India performed well in the political empowerment of women as it secured 65th rank globally. India scores within the top-10 on the head-of-state indicator (40.7%).
- India’s scores for women’s representation at the federal level, in ministerial positions (6.9%) and in parliament (17.2%), remain relatively low.
- In terms of the parity in the number of years with female/male heads of state for the last 50 years, India secured 10th rank.
iii.In the Health and Survival Index, India attained a score of 95.1%, slightly higher than in 2023 (95%)
Note: To achieve economic parity of 46% it is important to bridge gender gaps in estimated earned income (28.6%), legislative, senior officials, and management roles (14.4%), labour-force participation rate (45.9%) and professional and technical workers (49.4%).
India’s ranks in Subindex Ranks :
| Sub Index | Rank | Score 0-1 |
|---|---|---|
| Economic Participation and Opportunity | 142 | 0.398 |
| Educational Attainment | 112 | 0.964 |
| Health and Survival | 142 | 0.951 |
| Political Empowerment | 65 | 0.251 |
Global Gender Gap Performance: Region Wise
i.The 2024 Global Gender Gap Index shows that while no country has achieved full gender parity, 97% of the economies included in this edition have closed more than 60% of their gap, compared to 85% in 2006.
ii.The report groups the countries into 8 regions – Europe, North America, Latin America and the Caribbean, Eastern Asia and the Pacific, Central Asia, Sub-Saharan Africa, Southern Asia and Middle East and North America.
iii.Europe leads the 2024 regional gender gap rankings, having closed 75% of its gap in 2024. The top five European economies – Iceland, Finland, Norway, Sweden and Germany – all rank in the global top 10.
iv.Northern America shows a gender parity score of 74.8% ranking 2nd and Latin America and the Caribbean, with a gender parity score of 74.2% secured the 3rd rank while Eastern Asia and the Pacific (69.2%) and Central Asia (69.1%) raked 4th and 5th respectively.
Global Performance On 4 Dimensions of Gender Parity
i.Health and Survival has performed the best with 96% gap closed.
ii.Educational Attainment has shown significant progress in closing the 94.9% gap.
iii.Economic participation remains one of the most challenging areas, with 60.5% of the gender gap closed. Women globally are facing significant barriers in entering and advancing in the workforce.
iv.Political empowerment remains the area with the largest gender gap, with only 22.5% closed wherein women are still underrepresented in political leadership positions.
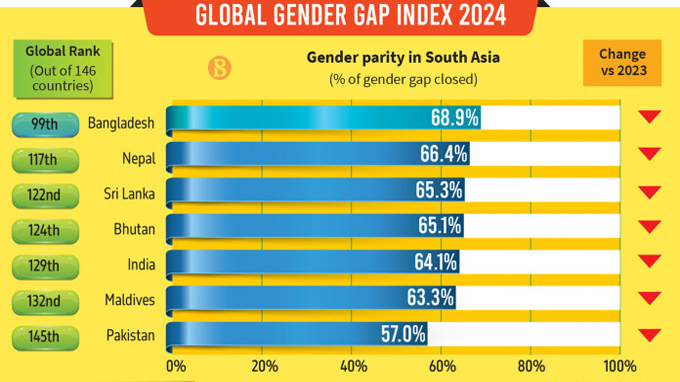
South Asia
In 2024, Southern Asia ranks seventh, with a gender parity score of 63.7%, the second lowest score economy of the eight regions.
| Economy | Regional Rank | Global Rank | Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bangladesh | 1 | 99 | 0.689 |
| Nepal | 2 | 117 | 0.664 |
| Sri Lanka | 3 | 122 | 0.653 |
| Bhutan | 4 | 124 | 0.651 |
| India | 5 | 129 | 0.641 |
| Maldives | 6 | 132 | 0.633 |
| Pakistan | 7 | 145 | 0.570 |
Note: Globally, Sudan was ranked last on the index while Pakistan slipped three places to 145th. India came within the economies with the lowest levels of economic parity, along with Bangladesh, Sudan, Iran, Pakistan, and Morocco. All of them registered less than 30% gender parity in estimated earned income.
About the Global Gender Gap Index:
i.The Global Gender Gap Index was first introduced by the WEF in 2006 to annually benchmark the present state and evolution of gender parity across four key dimensions: Economic Participation and Opportunity, Educational Attainment, Health and Survival, and Political Empowerment.
ii.The Global Gender Gap Index measures scores on a 0-100 scale and scores can be interpreted as the distance covered towards parity (i.e., the percentage of the gender gap that has been closed).
- A parity score of 1 indicates full parity. A gender gap is the distance from full parity.
iii.Further, the index evaluates a total of 101 countries that have been included in every edition of the index since 2006.
About the World Economic Forum(WEF):
Founder and Executive Chairman– Klaus Schwab
President– Børge Brende
Headquarters– Cologny, Switzerland
Establishment– 1971




