On May 05, 2020, China has successfully launched a powerful white-large cargo rocket ‘Long March 5B’and prototype spacecraft towards the space from the Wenchang Space Launch Center on the coast of southern China’s island province of Hainan at 6 p.m. (Beijing Time).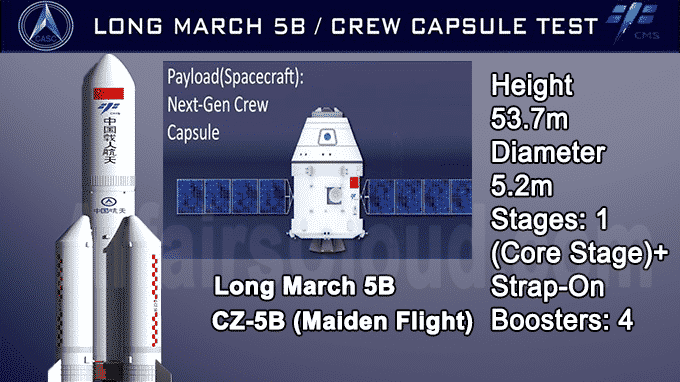 Key Points:
Key Points:
i.Trial:
- The test version of the new generation manned spacecraft and 176-foot-tall (53.7-meter) Long March 5B return capsule were sent for testing in space.It has a 5-metre-diameter core stage and four 3.35-metre-diameter boosters.It can carry a payload of 22 tonnes.
- Approximately 488 seconds later, the experimental manned spacecraft without crew, with a test version of the cargo return capsule, parted with the rocket and entered orbit as planned.
- This successful flight marked the beginning of the third phase of China’s manned space program, which is to build a space station.
ii.Aim:
- It was China’s ambitious major test to operate a permanent space station and send astronauts to the moon. The spacecraft will one day take astronauts to the space station, which China plans to complete by the year 2022 and finally on the moon. It will have the capacity to seat six crew members.
- While the cargo uses top technologies including non-toxic environmentally friendly fuels and a highly stable control system.
iii.US Vs China: The United States (US) is the only nation to have successfully sent humans to the moon. But China has made huge progress in its efforts to send astronauts to space, satellites in orbit and rovers to distant parts of the moon.
About Long March 5B:
Its lift capability to low Earth orbit is around 55,000 pounds, or 25 metric tons and has two hydrogen-fueled YF-77 core stage engines and eight kerosene-burning booster engines — with two engines mounted on four strap-on booster modules.
About China:
Capital– Beijing
Currency– Renminbi
President– Xi Jinping




