On January 28, 2020 in an effort to improve the conservation, restoration and rejuvenation of wetlands, the Ramsar Convention has declared 10 more wetland sites from India as sites of national importance. Ramsar sites are those which are declared under the Ramsar Convention signed in 1971 to preserve wetlands of national importance. Thus India now has a total of 37 Ramsar sites covering an area of 1,067,939 hectares.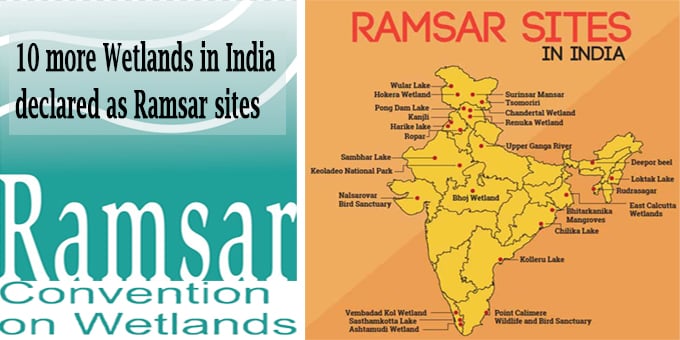 New Ramsar sites from India:
New Ramsar sites from India:
10 Ramsar sites: The 10 newly added Ramsar sites are as follows:
- Nandur Madhameshwar: This is the 1st Ramsar site of Maharashtra.
- Keshopur-Miani, Beas Conservation Reserve, Nangal: These 3 ramsar sites are newly added to Punjab. Apart from these 3 sites, Punjab already has 3 ramsar sites. Thus the total ramsar sites in the states counts to 6.
- Nawabganj, Parvati Agra, Saman, Samaspur, Sandi and SarsaiNawar: These 6 Ramsar sites have been newly added to Uttar Pradesh (UP) apart from 1 ramsar site it already had. Thus, UP now has 7 Ramsar sites.
Ramsar convention
i.It is the convention on wetlands formed by United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) in February 2, 1971 and came into force in 1975. The convention is named after Ramsar city of Iran where it was signed.
ii.This convention is one of the oldest inter-governmental accords signed by members countries to preserve the ecology of the wetlands. Those wetlands which are declared as Ramsar sites are protected by the strict guidelines as per the convention.
iii.Convention Aim: Through the convention it is aimed to maintain an international network of wetlands for conserving the biological diversity.
Wetlands:
i.A wetland is a distinct ecosystem flooded by water, either permanently or seasonally. Oxygen-free processes prevail in wetlands.
ii.They provide a wide range of resources and ecosystem services such as food, water, fibre, groundwater recharge, water purification, flood moderation, erosion control and climate regulation.
- Wetlands play a number of functions, including water purification, water storage, processing of carbon.
Environment ministry action plan:
The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change(MoEFCC) has prepared a 4 pronged strategy to restore wetlands. The strategy includes preparing baseline data, wetland health cards, preparing targeted Integrated Management Plans etc.
- The ministry will work closely with State Wetland Authorities to ensure wise use of Ramsar sites.
- Recently ministry launched ‘Nal se Jal‘ scheme in 2019 which aims to provide piped water connection to every household by 2024.
About Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change(MoEFCC):
Founded- 1985
Headquarters- New Delhi.
Union Minister- Prakash Javadekar.
Minister of State- Babul Suprio.





