Some basic info to understand the news better:
- Disarmament is the act of reducing, limiting, or abolishing weapons. Disarmament generally refers to a country’s military or specific type of weaponry. Disarmament is often taken to mean total elimination of weapons of mass destruction, such as nuclear arms/arsenal.
Now, the news:
- India and Pakistan are reportedly expanding their nuclear arsenal, despite a global trend towards disarmament, the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI) has said.
- The SIPRI on Monday published the findings in its ‘Yearbook 2015’, which assesses the current state of armaments, disarmament and international security in the world.
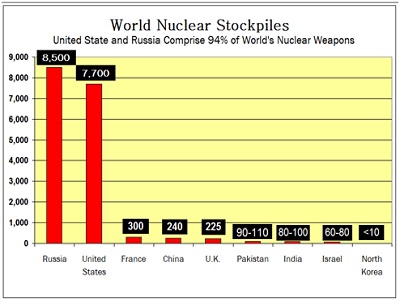
- The disarmament report prepared by the Swedish institute said that though the number of warheads fell from 22,600 to 15,850 between 2010 and 2015, India (90 to 100 warheads) and Pakistan (100 to 120 warheads) undertook “extensive and expensive long-term modernisation programmes”.
- According to the report, at the start of 2015, nine states – the United States, Russia, the United Kingdom, France, China, India, Pakistan, Israel and North Korea — possessed approximately 15,850 nuclear weapons, of which 4,300 were deployed with operational forces.
- The total number of nuclear warheads in the world is declining, primarily due to the US and Russia continuing to reduce their nuclear arsenal, albeit at slower pace compared with a decade ago, the report says.
Know more about this news topic:
- After the First World war , it was believed that the cause of the war had been the escalating buildup of armaments in the previous half century among the great powers . Thus, the Treaty of Versailles, signed after the war, effectively disarmed Germany, and a clause was inserted that called on all the great powers to likewise progressively disarm over a period of time. The newly formed League of Nations made disarmament an explicit goal in the ‘covenant of the league’
- Since the birth of the United Nations, the goals of multilateral disarmament and arms limitation have been deemed central to the maintenance of international peace and security. These efforts are supported by a number of key UN instruments. The Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons (NPT), the most universal of all multilateral disarmament treaties, came into force in 1970. The Chemical Weapons Convention entered into force in 1997, the Biological Weapons Convention in 1975. The Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty was adopted in 1996.
AffairsCloud Recommends Oliveboard Mock Test
AffairsCloud Ebook - Support Us to Grow
Govt Jobs by Category
Bank Jobs Notification