Note:
On 14th July 2023, ISRO successfully launched Chandrayaan-3 into orbit onboard the Launch Vehicle Mark-3 Mission 4 (LVM3 M4) rocket from SDSC SHAR (Satish Dhawan Space Centre-Sriharikota Range), Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh (AP) to Soft-land on the moon’s south pole.
About the Propulsion Module (PM):
i.The primary function of Chandrayaan-3’s PM was to carry the Lander and the Rover from the launch vehicle until the final lunar 100-km circular polar orbit.
ii.The main payload of PM is the Spectro-polarimetry of HAbitable Planet Earth (SHAPE), which is used to study the spectral and polarimetric measurements of Earth from the lunar orbit in the near-infrared (NIR) wavelength range (1–1.7 μm).
About the Propulsion module transfer mission:
i.The propulsion module separated the lander on 17th August 2023 and the lander successfully Soft-landed on the moon’s south pole on 23rd August 2023.
ii.After separating the lander and rover, the initial plan was to use PM’s payload, the SHAPE, to observe Earth from the circular polar orbit for about three months during the mission life of PM.
iii.There is an availability of over 100 kg of fuel in the PM after it moves around the moon orbit; this is the result of precise orbit injection by LVM3 and optimal earth / lunar burn maneuvers.
- The objective to move the PM around the orbit was to use the available fuel in the PM and derive additional information for future lunar missions.
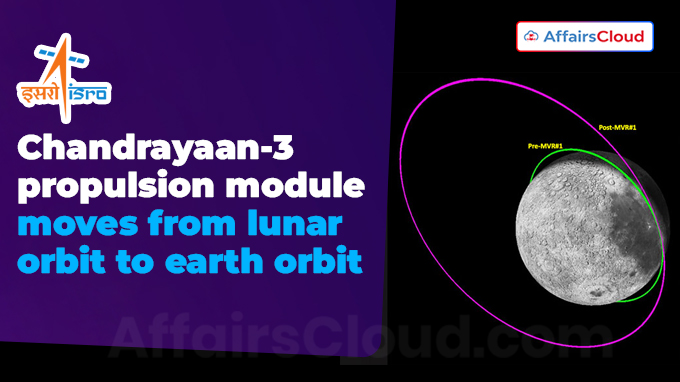
Methods used to Move PM from Moon orbit to Earth orbit:
i.ISRO performed three maneuvers, including the first orbit-rising maneuver (from 150 km to 5112 km), the second maneuver moved PM to Earth orbit of 1.8 lakhs x 3.8 lakhs km, and the final Trans-Earth Injection (TEI) maneuver.
ii.After the post-TEI maneuver, the propulsion module made four moon fly-bys (gravity assist maneuvers) before departing the Moon sphere of influence (SOI).
iii.The orbit period (time taken to revolve around Earth) of PM is nearly 13 days with a 27-degree inclination.
Outcome of the propulsion Module Transfer Mission:
This mission of PM to move from moon orbit to earth orbit will provide the following informative insights for future missions:
- To develop a software module to plan such a maneuver and its preliminary validation.
- To plan and execute a gravity-assisted flyby across a planet or celestial body.
- To avoid the uncontrolled crashing of the PM on the Moon’s surface at the end of its life, thus meeting the requirement of no debris creation.
ISRO set to launch India’s first X-Ray Polarimeter Satellite
ISRO is set to launch India’s first X-ray polarimeter satellite (XPoSat) to investigate the polarisation of intense astronomical X-ray sources.
- XPoSat is set to be launched by the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) from the Satish Dhawan Space Center in Sriharikota on December 2023.
- The mission life is expected to be approximately 5 years.
Mission objectives:
i.The measurement of X-ray polarization in the energy band of 8–30 keV (Kilo Electron Volts) emerging from X-ray sources.
ii.The long-term spectral and temporal studies of cosmic X-ray sources in the energy band of 0.8–15 keV.
Payloads:
i.It has two payloads, including the POLIX (Polarimeter Instrument in X-rays) and the XSPECT (X-ray Spectroscopy and Timing).
ii.POLIX is designed to measure polarimetry parameters such as the degree and angle of polarization in the medium X-ray energy range of 8–30 keV photons originating from astronomical sources.
- The POLIX payload is developed by the Raman Research Institute (RRI), Bengaluru, Karnataka, in collaboration with U R Rao Satellite Centre (URSC).
iii.XSPECT payload will provide spectroscopic information within the energy range of 0.8–15 keV.
- The XSPECT payload was developed by the URSC.
Note:
i.Light is an electromagnetic wave in which both electric and magnetic field vibrations occur perpendicular to each other. Polarized waves are light waves in which the vibrations occur in a single plane.
ii.The process of transforming unpolarized light into polarized light is known as polarization, one of the intrinsic properties of light.
Uses of X-Ray Polarimeter:
X-Ray polarization serves as a crucial diagnostic tool for examining the radiation mechanism and geometry of celestial sources.
Recent Related News:
i.On 2nd September 2023, the Indian Space Research Organisation(ISRO) launched Aditya-L1(Lagrange Point 1), India’s 1st observatory-class space-based solar mission, launched by PSLV-C57 (Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle) rocket from the Second Launch Pad (SLP), Satish Dhawan Space Centre – SDSC (formerly Sriharikota Range – SHAR) in Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh(AP).
ii.On 26th August 2023, Prime Minister (PM) Narendra Modi declared that 23rd August of every year will be observed as “National Space Day” in India to commemorate the soft landing of Chandrayaan 3 on the Moon.
About the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO):
Chairman– S. Somanath
Headquarters– Bengaluru, Karnataka
Establishment– 1969